CryptQ is all about innovation and technology development. Here we would like to provide a look into the basics of quantum key distribution, some insights into how we aim to translate that into technology, and an update on the current status of the hardware development effort.
The aim of the project is to build a CVQKD encryption system as depicted below. It consists of a transmitter and a receiver connected by an optical fibre. A coherent quantum state of light is selected at random from a predefined ensemble. The generated quantum state is sent over the fibre channel to the receiver that performs coherent detection. The measurement result is transformed back into the secret key by employing post-processing algorithms. The secret keys are stored in a key management system (KMS) from where they can be retrieved by the AES256 data encryptor performing e.g. 100 Gbit/s secure optical communication.
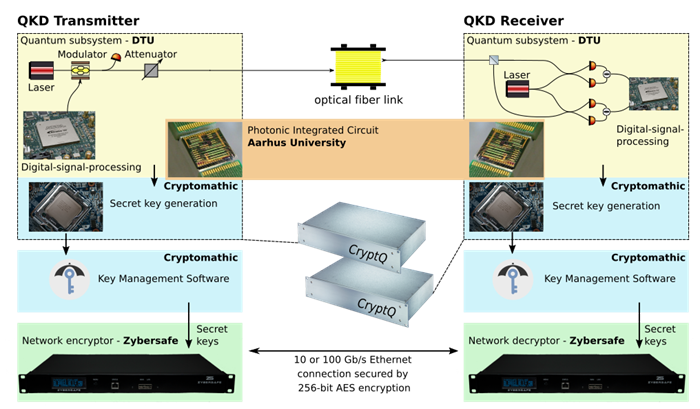
In CryptQ, the consortium of 2 academic partners, 3 industry partners and 1 GTS institute together with two end-users, will leverage its unique combination of complementary and highly relevant competences to realize a CVQKD system that can run autonomously in a realistic environment. DTU has a leading role in CVQKD research having built the proof-of-concept QKD lab prototype. Zybersafe is a supplier of encryption equipment with a keen interest in quantum technologies. In CryptQ, DTU and Zybersafe will develop the lab prototype to a demonstrator capable of autonomous operations. Zybersafe will develop an AES encryption system able to work with quantum enhanced encryption. Using their strong expertise in classical cryptography and key management, Cryptomathic will be responsible for building the protocol stack for key generation and the KMS. The Danish Metrology Institute (DFM) is the only national metrology institute in the world with expertise in CV quantum optics. In CryptQ, DFM will perform a validation of the demonstrator. Aarhus University (AU) will design and fabricate photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for CryptQ